Investigating Interfacial Phenomena
 |
| Contour analysis of drops |
| Photo: HZDR/Detlev Müller |
When in water immersed particles adhere to gas bubbles, three different phases are in contact: a solid, a liquid and a gaseous phase. By precisely characterizing their properties at microscopic scale, HIF scientists aim at improving the general understanding of interfacial phenomena. A better understanding will thus help to improve controlling the flotation processes. For example, by using amphiphilic molecules - flotation reagents that are soluble in both polar solvents (e.g., fats) and nonpolar solvents (e.g., water).
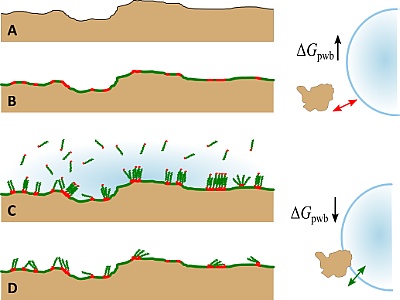 |
| Mental experiment: Hydrophobization of a mineral surface and the successful attachment of a gas bubble |
Important questions the Processing Department is tackling:
- Which fundamental physical parameters describe the particles wettability the best?
- How do hydrophobic interactions work?
- What is the impact the heterogeneity of a surface has on its functionality and particle-bubble interactions?
- What role do water structure effects play in particle-bubble interactions of hydrophilic and hydrophobic phases?
- Why do some depressant reagents have an additional promoting effect on hydrophobized particles?
 |
| Surface energy determination |
| Photo: HZDR/Detlev Müller |
The following methods are being used in order to address those questions:
- Tensiometry (static und dynamic) using a bubble pressure tensiometer and the pendant drop method
- Wettability measurements with contour analysis
- Film compression measurement using a Langmuir-Blodgett trough
- Adsorption measurements using a quartz crystal microbalance
- Streaming potential determination with an automatic titration and a Zeta potential analysis
- Dynamic frothing analyses
- Surface energy determination using the inverse gas chromatography (iGC) technique
Selected Publications
- Rudolph M.; Hartmann, R.
"Specific Surface Free Energy Component Distributions and Flotabilities of Mineral Microparticles in Flotation – An Inverse Gas Chromatography Study", Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 513 (2017) 380-388
DOI-Link: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.10.069
- Knüpfer, P.; Fritzsche, J.; Leistner, T.; Rudolph, M.; Peuker, U. A.
"Investigating the removal of particles from the air/water-interface – Modelling detachment forces using an energetic approach", Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 513(2017)
DOI-Link: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.10.046

